NORbert is an open source alternative to the Dediprog EM100Pro. If you do firmware development you probably know the EM100: you plug it in where a SPI NOR flash chip sits, load a firmware image over USB and it pretends to be a real flash chip to the SoC. It's great but it costs around $500 which is a lot if you just want to hack on open source firmware.
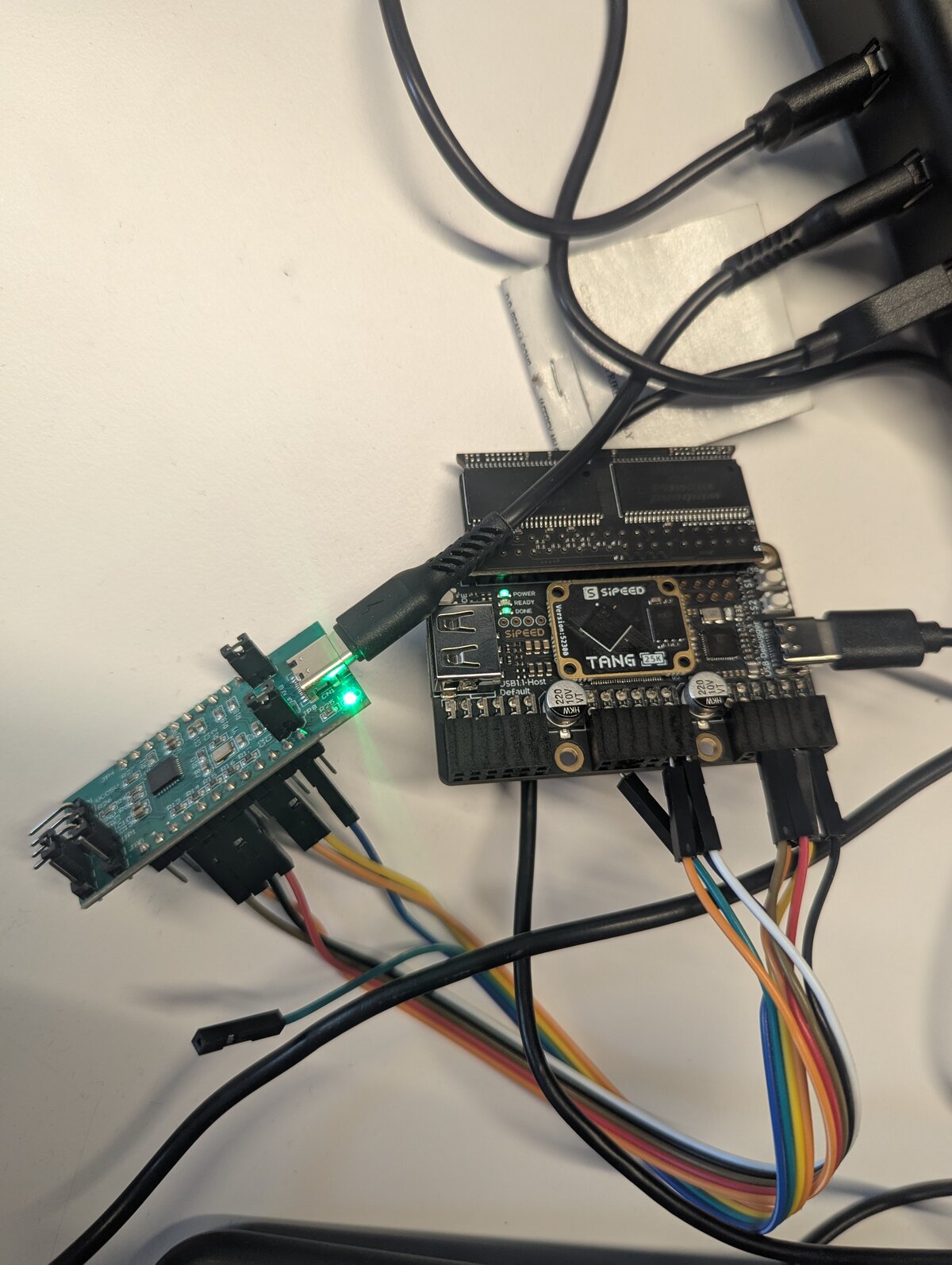
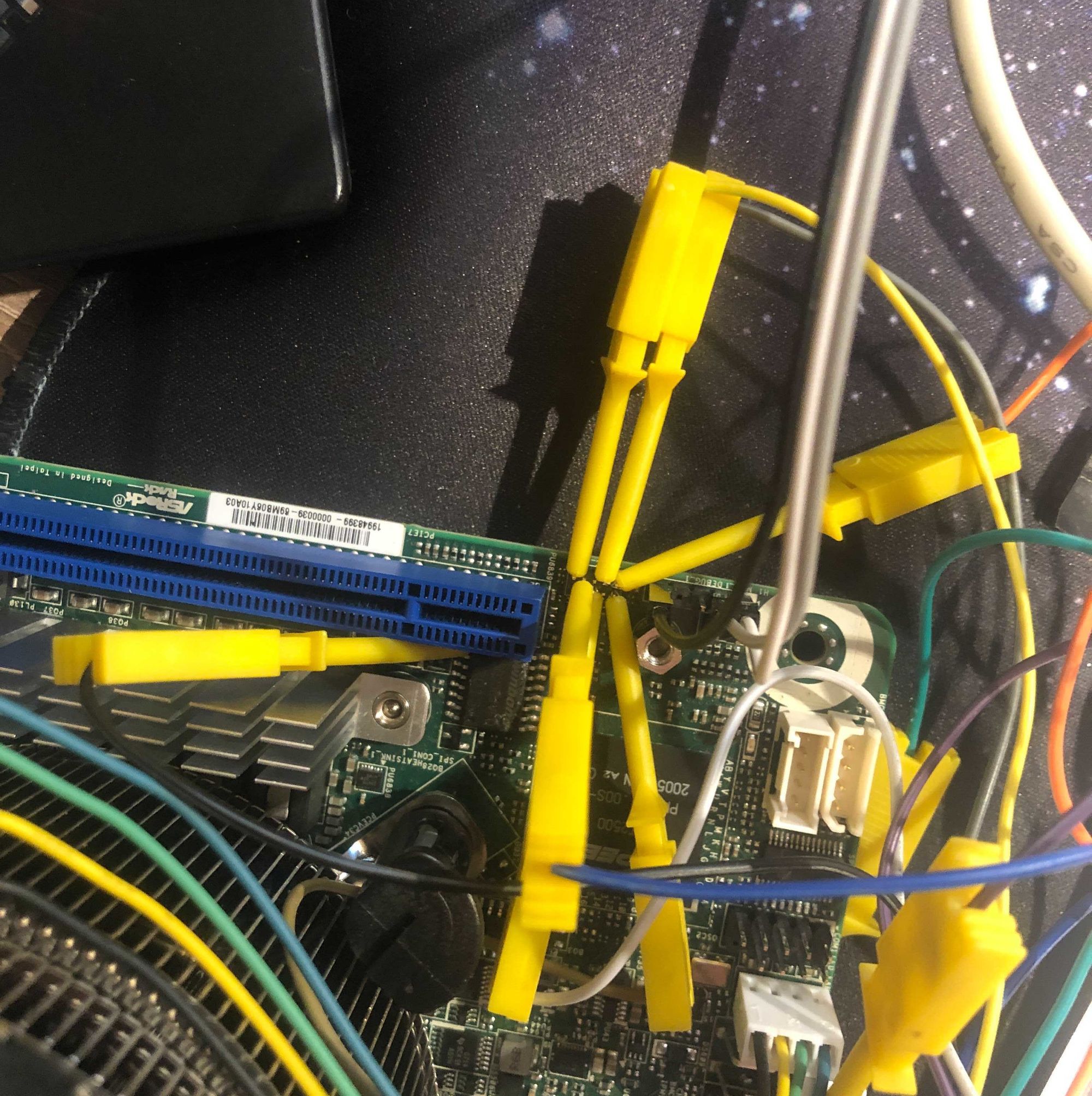
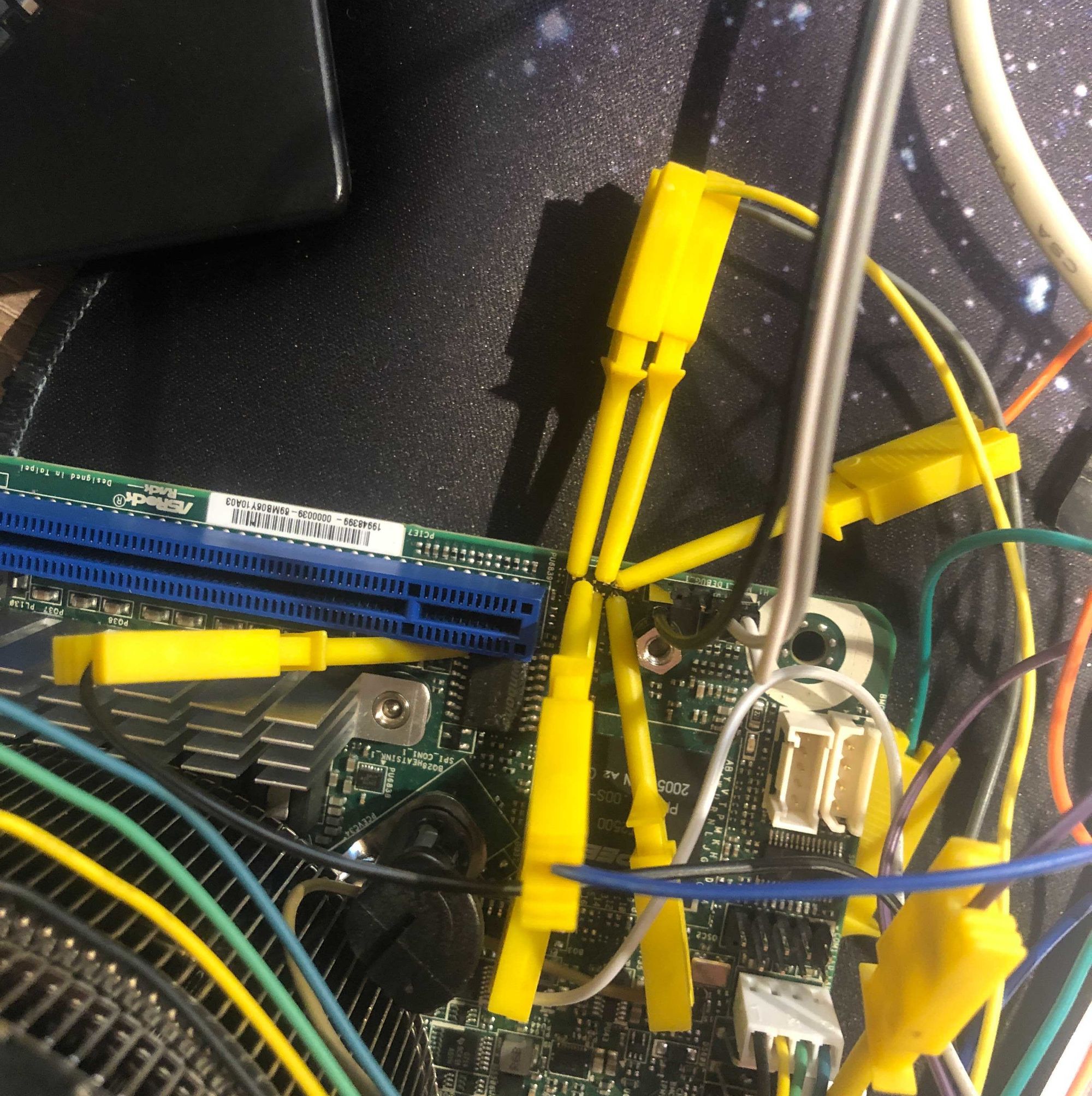
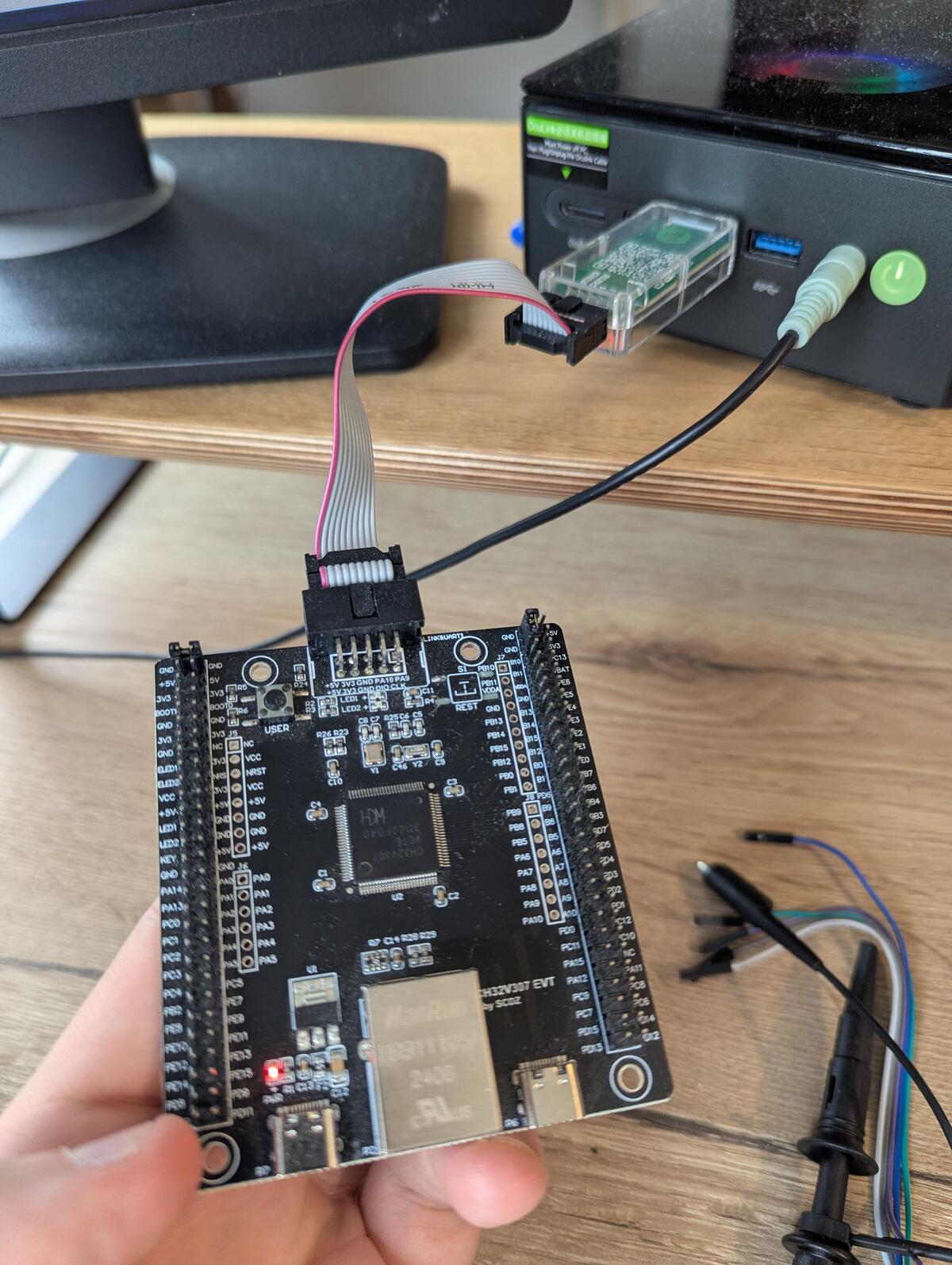
The FPGA with SDRAM board attached to an FT4222 which can do single, dual and quad SPI I/O.
The hardware
The setup is a Sipeed Tang Primer 25K (Gowin GW5A-LV25MG121) with the dock ext-board that has two SDRAM chips (64MB total) and a USB-UART bridge. The SDRAM backs the emulated flash contents using a bit-interleaved storage scheme across both chips so you get zero-overhead serial output. The SPI signals come out on PMOD connector J5.
The BOM is pretty cheap compared to an EM100. The Tang Primer 25K goes for around $25, the SDRAM dock board is about $10, and an FTDI breakout is another $10-15. So you're looking at roughly $45-50 for a working SPI flash emulator. That's about a tenth of what an EM100 costs and I think that makes a real difference for getting more people into open source firmware work.
Chip configuration with RON files
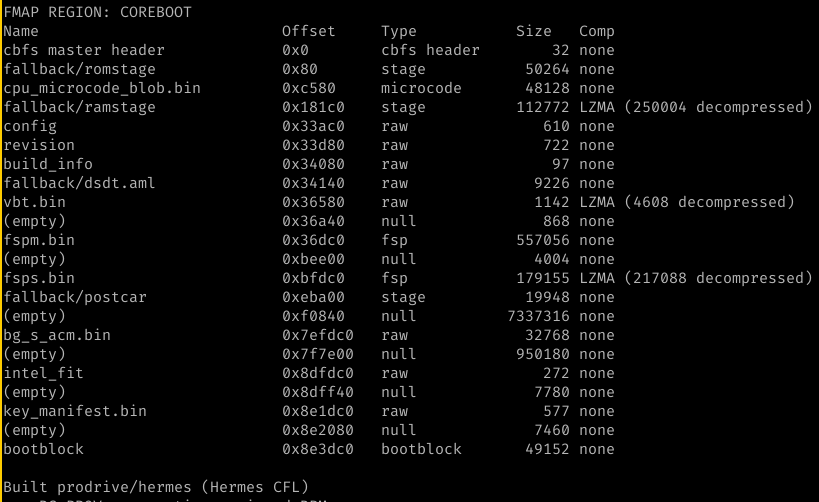
This is the part I'm happy about. In flashprog, all flash chip definitions live in a single flashchips.c – nearly 27,000 lines of C struct initializers. For rflasher I converted all of that to RON (Rusty Object Notation) files, one per vendor. RON is just data. No function pointers, no magic macros, just human-readable chip definitions with JEDEC IDs, sizes, erase block layouts and feature flags.
NORbert uses these same RON chip definitions from rflasher's chip database. You run spi-flash-tool configure W25Q128JV, the host tool loads the RON file, extracts the JEDEC ID and supported features, generates an SFDP table and sends it to the FPGA over UART. Then NORbert presents itself as that chip to whatever SPI master is connected. You can impersonate any of the 482+ chips in the database without rebuilding the bitstream.
Loading and reading: UART now, FT2232H WIP
Right now the out-of-band channel for loading and reading back flash contents is UART at 2 Mbaud. That's what the dock board's USB-UART bridge gives you. You can load images, dump contents, verify writes and configure chip identity over it. It works but loading a full 16MB image takes a while at that speed.
I have an FT245 available but what I'm working on now is using an FT2232H for fast loading. Its synchronous FIFO mode can do 25+ MB/s which would bring a 16MB load down to under a second. This is WIP.
The SPI interface on the PMOD connector is the other side – that's what your target system sees as the flash chip.
Open source toolchain
Right now NORbert needs the Gowin proprietary IDE for synthesis and place-and-route. But open source support for Gowin FPGAs is coming along in the Apicula project. There's been a lot of recent work on GW5A support, which is the FPGA family the Tang Primer 25K uses:
- #388: GW5A PLL implementation
- #412: GW5 ADC implementation
- #450: DLLDLY support, PINCFG validation, GW5AST BSRAM handling
- #466: GW5AST-138 reset fix
- #473: tm_parser fixes
- #476: Latch pack/unpack support
- #480: Support loading device from JSON
Once Apicula can handle PLLs, SDRAM and SPI on the GW5A the entire stack from RTL to bitstream will be fully open source.
Upcoming PMOD addon board
There's a board in the works that should make NORbert a lot more practical to use day to day. The idea is a dedicated PCB with a nice header like the EM100 has for exposing the flash lines to clip onto a target board, an onboard FT2232H for fast image loading, and voltage level shifters for 1.8V and 3.3V targets. It plugs into the PMOD headers on the Tang Primer 25K dock.
9elements is designing this board. No hard promises on when it'll be ready, but it would make NORbert a pretty complete EM100 replacement.
Conclusion
NORbert is still early but it works. If you have a Tang Primer 25K with the SDRAM dock board you can build and try it today. The code is on GitHub: NORbert.